With rising concerns over fossil fuel depletion and environmental pollution, the world is shifting toward renewable energy solutions. One such promising opportunity is producing ethanol from waste grains. Ethanol is a clean-burning biofuel widely used in fuel blending, pharmaceuticals, beverages, and chemical industries. Utilizing agricultural waste, especially surplus or non-edible grains, provides an eco-friendly and cost-effective method for ethanol production—turning food waste into valuable energy.
Contents
- 1 Why Start a Business in Ethanol Production from Waste Grains?
- 2 What is Ethanol from Waste Grains?
- 3 Types of Waste Grains Suitable for Ethanol Production
- 4 Process of Producing Ethanol from Waste Grains
- 5 Required Equipment and Machinery
- 6 Infrastructure and Space Requirement
- 7 Legal Compliance and Licenses
- 8 Cost and Profitability
- 9 Environmental and Economic Benefits
- 10 Target Markets and Buyers
- 11 Challenges and Risk Management
- 12 Future Scope and Scalability
- 13 Final Thoughts
Why Start a Business in Ethanol Production from Waste Grains?
India generates massive amounts of agricultural residues and waste grains every year. Much of it goes unused or decomposes. These grains, although unfit for human consumption, are rich in carbohydrates and can be efficiently fermented to produce ethanol.
Starting a business in this domain not only reduces environmental waste but also supports the government’s biofuel targets and the Ethanol Blending Program (EBP). Entrepreneurs have the opportunity to create a sustainable business while contributing to India’s green energy goals.
Visit this Page for More Information: Start a Business in Ethanol Industry
What is Ethanol from Waste Grains?
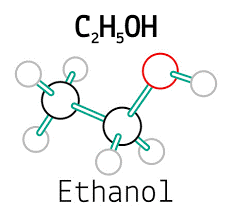
Ethanol, or ethyl alcohol, is a type of renewable alcohol-based biofuel derived from the fermentation of sugars and starches. Waste grains, such as spoiled wheat, broken rice, damaged maize, or unfit pulses, are rich in fermentable sugars.
These grains are processed through hydrolysis and fermentation to convert starch into ethanol. The resulting product can be used as:
-
Fuel blend (e.g., E10, E20 for vehicles)
-
Base for hand sanitizers and disinfectants
-
Ingredient in alcoholic beverages
-
Raw material for chemical industries
The conversion of waste into fuel offers environmental, economic, and energy-security benefits.
Related Business Plan: Ethanol Manufacturing as Bio-Fuel
Types of Waste Grains Suitable for Ethanol Production
The following categories of grains can be used:
-
Broken or damaged rice
-
Spoiled wheat and maize
-
Rotten sorghum or millets
-
Wet or pest-infested pulses
-
Brewer’s spent grains
-
Unsold or aged stock from food processing units
These grains are typically considered agricultural waste and are available at low or zero cost, making them an ideal raw material for ethanol production.
Read Similar Articles: ETHANOL AND ALCOHOL INDUSTRY
Process of Producing Ethanol from Waste Grains
The ethanol production process from waste grains involves several stages:
-
Grinding and Slurrying – Grains are crushed and mixed with water to create a slurry.
-
Liquefaction – Enzymes are added to break down starch into dextrins.
-
Saccharification – Further enzymes convert dextrins into simple sugars.
-
Fermentation – Yeast is introduced to convert sugars into ethanol.
-
Distillation – The fermented mixture is distilled to separate ethanol from water.
-
Dehydration and Purification – Ethanol is refined to fuel-grade quality.
-
Byproduct Management – Solid residues (distiller’s dried grains) are processed as cattle feed.
This process is scalable, eco-friendly, and can be integrated into existing agro-industrial setups.
Click here to send your queries/Contact Us
Required Equipment and Machinery
To start an ethanol production unit using waste grains, the following machinery is needed:
-
Grain crusher and slurry mixer
-
Liquefaction tank with agitators
-
Fermenters with temperature control
-
Distillation columns
-
Dehydration system (molecular sieve or membrane unit)
-
Storage tanks and bottling unit
-
Effluent treatment plant (ETP)
Modern automated plants reduce manual labor and improve safety and productivity.
Related Feasibility Study Reports: Opportunities In Business Of Ethanol As Bio-fuel
Infrastructure and Space Requirement
Setting up a small to medium-scale ethanol plant requires approximately 10,000 to 20,000 sq. ft. of land. This space accommodates:
-
Raw material and storage sheds
-
Process and fermentation areas
-
Distillation and dehydration zones
-
Laboratory and quality control rooms
-
Office, loading dock, and security zone
Proximity to agricultural hubs or food processing units ensures a consistent waste grain supply.
Read our Books Here: Maize (Corn) Processing
Legal Compliance and Licenses
To legally produce ethanol in India, the following permissions and licenses are mandatory:
-
Ethanol manufacturing license from State Excise Department
-
Pollution Control Board NOC
-
Factory License and Fire Safety Clearance
-
Environment Impact Assessment (EIA), if required
-
BIS certification for fuel-grade ethanol
-
FSSAI license (if producing food-grade ethanol)
-
Udyam/MSME registration and GST
Obtaining proper legal clearances helps avoid regulatory hurdles and ensures smooth operations.
Click here to send your queries/Contact Us
Cost and Profitability
The investment needed to establish a 30 KLPD (Kilo Liters per Day) ethanol plant using waste grains ranges from ?15 crore to ?25 crore, depending on scale and automation.
Cost elements include:
-
Land and infrastructure
-
Plant and machinery
-
Enzymes and yeast
-
Licensing and approvals
-
Power and water supply
-
Working capital and labor
Despite the upfront cost, the business offers excellent ROI. With government incentives under the Ethanol Blending Program and consistent demand, profit margins can exceed 20%–30%, with the breakeven period typically within 4–5 years.
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Producing ethanol from waste grains benefits the environment by:
-
Reducing landfill and methane emissions
-
Lowering fossil fuel dependence
-
Converting waste into renewable energy
-
Providing income to farmers and food processors
-
Creating green jobs in rural areas
Target Markets and Buyers
Ethanol has a vast and growing customer base, including:
-
Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) like IOCL, BPCL, HPCL
-
Alcohol beverage companies
-
Pharmaceutical and sanitizer manufacturers
-
Chemical processing industries
-
Cattle feed and fertilizer companies (for byproducts)
-
Exporters of biofuel and ethanol blends
Long-term supply contracts with OMCs provide predictable revenue streams.
Challenges and Risk Management
Challenges:
-
Raw material availability during off-seasons
-
Complex licensing and regulatory compliance
-
High initial capital investment
-
Effluent treatment and environmental monitoring
Solutions:
-
Source from multiple grain suppliers and FCI
-
Consult experts for obtaining licenses and EIA reports
-
Apply for government subsidies and soft loans
-
Install a proper ETP and monitor emissions regularly
Proactive planning and efficient management reduce risks significantly.
Future Scope and Scalability
With India targeting 20% ethanol blending by 2025, there is massive demand for domestic ethanol production.
Cellulosic ethanol (from crop residues)
-
Export of bioethanol to fuel-deficient countries
-
Technology upgrades (continuous fermentation, membrane distillation)
-
Integration with bio-CNG and solar power systems
The sector offers long-term growth with environmental sustainability and profitability.
Final Thoughts
Producing ethanol from waste grains is a high-potential business that transforms agro-waste into clean energy. With government support, robust demand, and eco-friendly processes, it offers entrepreneurs a rare opportunity to combine purpose and profit. As India and the world shift to sustainable energy solutions, ethanol production will remain a key pillar of the green economy.
Reasons for Buying NIIR Report:
- Our research report helps you get a detailed picture of the industry by providing an overview of the industry along with the market structure and classification.
- Our report provides market analysis covering major growth driving factors for the industry, the latest market trends and the regulatory framework of the industry.
- Our Report provides an analysis and in-depth financial comparison of major Players / Competitors.
- Our Report provides indispensable buyers’ data with their company financials as well as the contact details, which can be an important tool in identifying the target customers.
- Our report provides forecasts of key parameters which help to anticipate the industry performance.
- We use reliable sources of information and databases.
See More Links:
- Start a Business in Asia
- Start a Business in Potential Countries for Doing Business
- Best Industry for Doing Business
- Business Ideas with Low, Medium & High Investment
- Looking for Most Demandable Business Ideas for Startups
- Startup Consulting Services