The India-EU Free Trade Agreement Opportunities for MSME Entrepreneurs represent one of the most significant structural shifts for Indian manufacturing and export-oriented entrepreneurship in recent decades. This agreement is not a diplomatic headline meant for policy circles alone. It directly reshapes cost structures, market access, and feasibility outcomes for industrial projects across multiple sectors.
For business investors, MSME promoters, and first-generation manufacturers, the agreement introduces a rare advantage: predictability. Clearly defined tariff elimination schedules, product-specific rules of origin, and improved access to European buyers allow entrepreneurs to evaluate projects using hard commercial logic rather than assumptions. With a combined market exceeding INR 2091.6 lakh crore, the opportunity is substantial—but only if approached with discipline.
Contents
- 1 Why the India-EU Trade Agreement Changes Business Viability
- 2 Market Access as a Project Selection Filter
- 3 Labour-Intensive Manufacturing and the MSME Advantage
- 4 Textiles and Apparel: Zero Duty, High Discipline
- 5 Leather and Footwear Manufacturing Opportunities
- 6 Marine Products and Value-Added Seafood Processing
- 7 Engineering Goods and Value Chain Integration
- 8 Chemicals, Plastics, and Rubber Manufacturing
- 9 Critical Success Factors Entrepreneurs Cannot Ignore
- 10 conclusion
Why the India-EU Trade Agreement Changes Business Viability
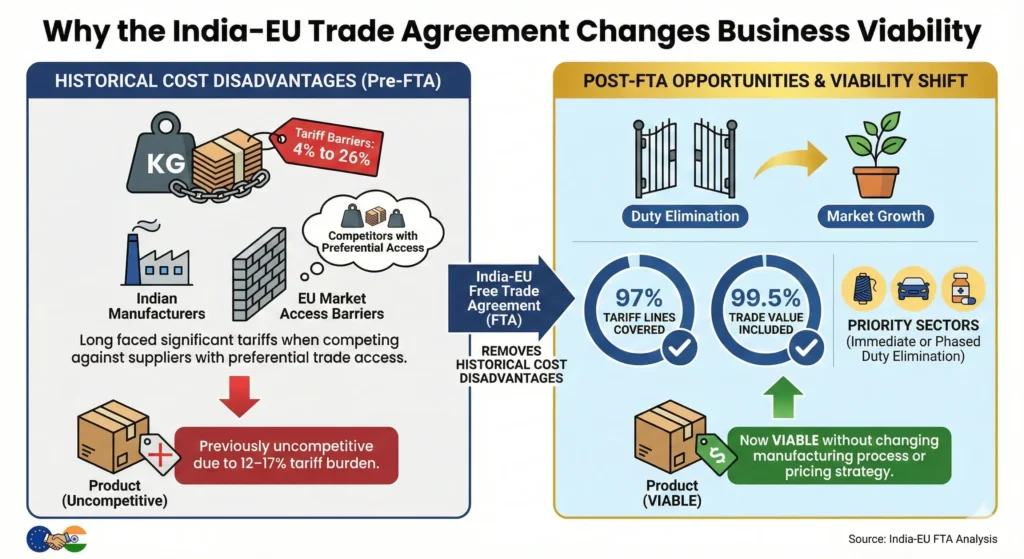
The most important shift created by the India-EU Free Trade Agreement opportunities is the removal of historical cost disadvantages. Indian manufacturers have long faced tariff barriers ranging from 4% to 26% when competing in the European Union against suppliers from countries with preferential trade access.
Under the agreement:
- 97% of tariff lines are covered
- 99.5% of trade value is included
- Multiple priority sectors receive immediate or phased duty elimination
This fundamentally alters feasibility calculations. A product that was previously uncompetitive due to a 12–17% tariff burden can now be viable without changing its manufacturing process or pricing strategy.
View our:- Books
Market Access as a Project Selection Filter
Market access is not an abstract trade concept. For entrepreneurs, it is a project selection filter.
Under the agreement, sectors receiving day-one tariff elimination become immediately viable for export-oriented manufacturing:
- Textiles and apparel
- Leather and footwear
- Marine products
- Gems and jewellery
- Sports goods and toys
These sectors already have established domestic supply chains, measurable EU demand, and fragmented supplier bases. The cost barrier has been legislatively removed. What remains is execution capability.
Labour-Intensive Manufacturing and the MSME Advantage
Labour-intensive sectors sit at the core of the India-EU Free Trade Agreement opportunities, aligning naturally with India’s workforce profile and MSME ecosystem.
Textiles, apparel, marine products, toys, and sports goods together account for exports exceeding INR 2.87 lakh crore that previously faced EU duties between 4% and 26%. These duties are now eliminated or significantly reduced.
Common characteristics that favour MSMEs include:
- Moderate capital intensity
- Dependence on skilled and semi-skilled labour
- High sensitivity to landed cost
- Buyer-driven demand visibility
Indian exporters have already demonstrated global competitiveness in these sectors. The agreement simply removes the structural penalty.
Read More Article:- Investment Opportunities
Textiles and Apparel: Zero Duty, High Discipline
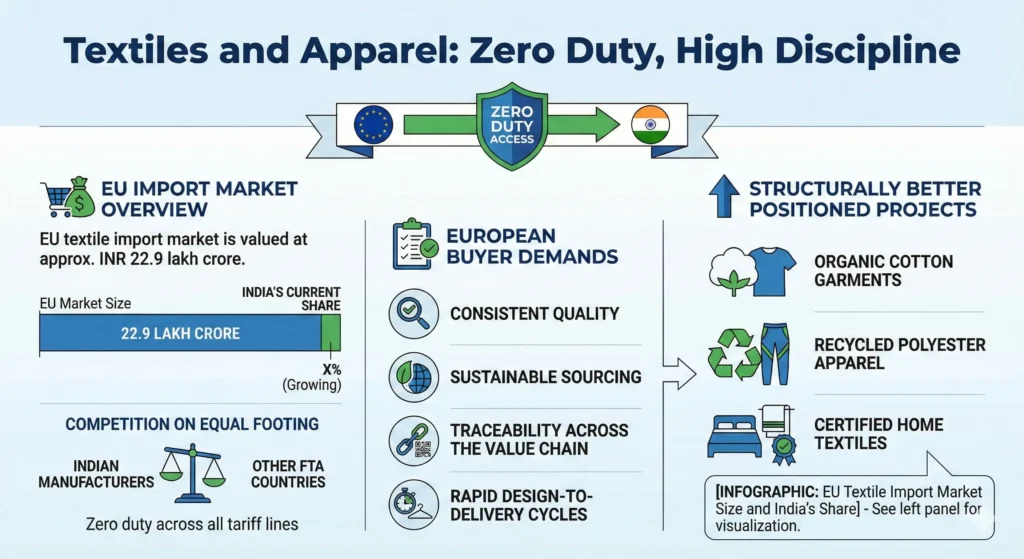
The EU textile import market is valued at approximately INR 22.9 lakh crore. With zero duty access across all tariff lines, Indian manufacturers now compete on equal footing with suppliers from other FTA countries.
However, access alone does not guarantee orders. European buyers demand:
- Consistent quality
- Sustainable sourcing
- Traceability across the value chain
- Rapid design-to-delivery cycles
Projects focused on organic cotton garments, recycled polyester apparel, and certified home textiles are structurally better positioned to capture this demand.
View:- Project Report
Leather and Footwear Manufacturing Opportunities
Before the agreement, Indian leather exporters faced tariffs of up to 17%. These tariffs are now fully eliminated.
The European Union imports leather and footwear worth INR 8.71 lakh crore annually, while India’s share remains modest. Even a marginal increase in market penetration translates into substantial incremental revenue.
New entrants gain an advantage if they focus on:
- Design-led product portfolios
- Environmentally compliant tanneries
- Strict adherence to EU chemical and labelling norms
At scale, production above 10,000 pairs per month with factory-level gross margins of 35–40% is achievable under disciplined operations.
Marine Products and Value-Added Seafood Processing
Marine exports receive 100% trade value coverage under the agreement, eliminating tariffs of up to 26%. The EU marine import market is valued at INR 4.67 lakh crore.
Commercially viable project models include:
- Shrimp processing plants
- IQF frozen seafood facilities
- Value-added fish and seafood products
Success depends on raw material sourcing discipline, cold chain infrastructure, and certifications such as BRC and IFS. While capital requirements are higher (INR 3–5 crore), net margins of 8–12% are realistic for compliant and well-managed operations.
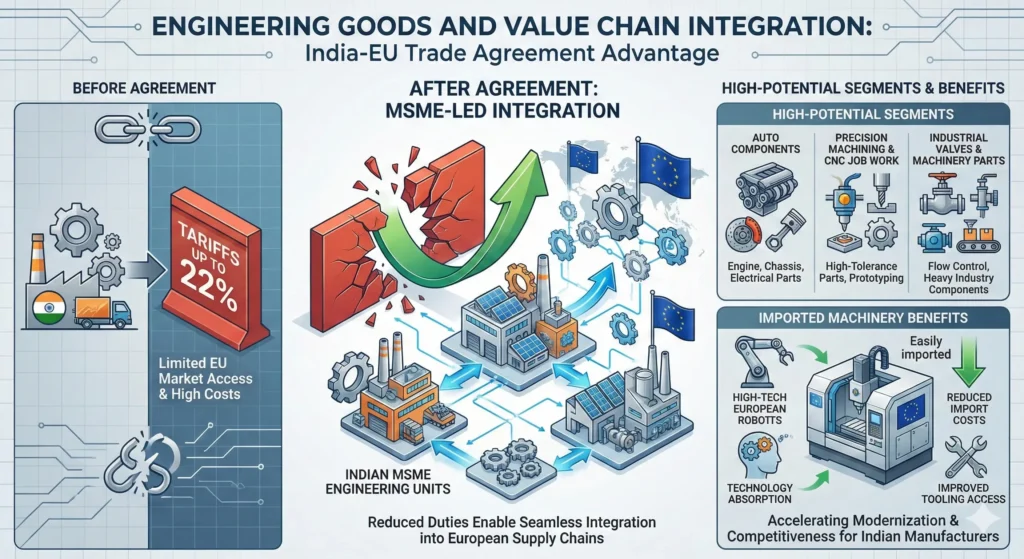
Engineering Goods and Value Chain Integration
Engineering goods exports to the EU previously faced tariffs of up to 22%. Reduced duties now enable MSME-led engineering units to integrate into European supply chains.
High-potential segments include:
- Auto components
- Precision machining and CNC job work
- Industrial valves and machinery parts
The agreement also reduces costs on imported European machinery, improving tooling access and technology absorption for Indian manufacturers.
Chemicals, Plastics, and Rubber Manufacturing
The agreement eliminates duties on 97.5% of India’s chemical export basket by value, addressing tariffs of up to 12.8%. The EU chemical import market alone is valued at INR 43.57 lakh crore, with plastics and rubber adding another INR 27.67 lakh crore.
These sectors favour technically competent promoters with:
- Strong process control
- Regulatory compliance capabilities
- Focus on niche molecules or formulations
Entry barriers are higher, but defensibility and long-term buyer relationships are stronger.
Critical Success Factors Entrepreneurs Cannot Ignore
The India-EU Free Trade Agreement opportunities remove tariff barriers, not operational requirements.
European buyers are unforgiving when it comes to:
- Quality deviations
- Shipment delays
- Compliance failures
Common failure points include underestimated working capital needs, insufficient certification planning, and over-dependence on a single buyer. Export payment cycles of 60–90 days must be planned into project financials from day one.
Watch:- Youtube Channel
conclusion
If you are evaluating a manufacturing or export-oriented project under the India-EU framework, a professionally prepared feasibility study, plant setup advisory, and compliance roadmap can determine viability before capital is committed.
How NPCS Can Help You
NPCS provides end-to-end project consultancy for MMA and other chemical manufacturing projects, including:
- Detailed Project Reports (DPRs)
- Techno-economic feasibility studies
- Process flow & plant layout design
- Machinery & vendor identification
- Costing, profitability & break-even analysis
- Licensing & regulatory guidance
Niir Project Consultancy Services
106-E, Kamla Nagar, Opp. Mall ST,
New Delhi-110007, India.
Email: info@entrepreneurindia.co
Mobile: +91-9097075054
Website:https://www.entrepreneurindia.co